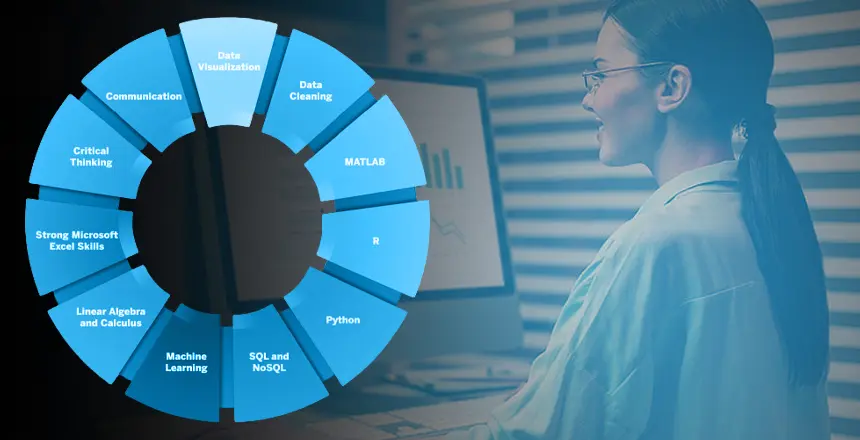
Business analyst skills
1. Analytical Thinking and Problem-Solving
Examining the subject critically:
Analysts (BAs) must be able to analyze intricate issues, assess facts, and suggest reasoned answers. This means breaking down challenges into components that are simpler and easier to handle.
Concentration on Accuracy:
They should carefully scrutinize information, procedures, or operation modes so as to retain correctness and thus prevent blunders from appearing in their evaluations.
2. Technical Proficiency
Data Investigation and Picturesque Methods:
Getting used to Microsoft Excel, SQL, Tableau, and Power BI tools is necessary for identifying data tendencies and presenting them in a way that can be understood by everyone else.
Software Development Understanding:
Understanding the software development life cycle (SDLC) will enable BAs to communicate effectively with the IT teams, thereby ensuring that their business requirements are catered for.
3. Communication skills
Verbal Communication:
It is essential for a BA to express thoughts and demands with clarity with regard to stakeholders, other team members, or clients. It plays a big role in convincing all involved parties.
On Paper:
The concise nature of the reports , possibility documents, and user tales serves as a critical part that guarantees all parties are aware of the business wants.
4. Negotiation and Persuasion
Stakeholder Management:
Business analysts frequently act as mediators between conflicting stakeholders. The capacity to negotiate and persuade various parties is crucial for achieving a consensus beneficial to the whole project.
Influence:
Additionally, a BA needs to influence decision-makers in order for them to accept the recommendations made by him or her instead of merely stating statistics.
5. Project Management
Time Management:
It is essential for BAs to avoid wasting time on unnecessary activities while focusing on things that matter most, thus ensuring a smoother flow of events until completion dates are reached.
They help in reducing costs; hence, BAs will identify potential risks ahead in order to avoid problems during the implementation phase.
6. Business knowledge
Knowledge of an Industry:
BAs are able to make proper decisions that are in accordance with industry norms and trends, given their extensive grasp of the unique industry they work in.
Business Acumen:
Knowing finance basics and indicators aids in assessing how much the solution is economically sensible.
Business Acumen:
Knowing finance basics and indicators aids in assessing how much the solution is economically sensible.
7. Interpersonal Skills
Empathy is an important skill commonly used by BAs when they are talking or communicating with their stakeholders, since it helps them tune their messages and even redesign their solutions. On the other hand, if you want a project to be successful, you must collaborate with diverse teams whose members come from different functions, for instance, IT specialists, marketing professionals, and finance professionals.
8. Problem-Definition and Requirement Gathering
In the requirements elicitation process, business analysts usually interact with or rather involve different groups of persons who are doing business to be able to discover all the needs of a business so that its proposed solution may be suitable. The term gap analysis means that business analysts (BAs) need to check the existing situation and what they want so as to come up with a plan on how such differences can be closed down between these two points.
9. Adaptability and Flexibility
Change Management:
A business analyst should be able to manage any changes that may occur in organizational requirements, technology, or the marketplace. In this respect, feedback should be considered an opportunity for improvement, and the plans should be modified accordingly.
Agility:
Being agile entails having the ability to respond promptly to changes in business dynamics and take advantage of new situations with speed.
10. Decision-Making and Judgment
Prioritization:
It is the responsibility of BAs to rank their responsibilities and choices according to their effect on the business and how critical they are at that time.
Judgment:
A big part of what a BA does is make informed decisions by collecting and analyzing various data as well as listening to their clients’ views.
Conclusion
There is a lot of work performed by a business analyst who needs a variety of special abilities (technical), business acumen, and communication skills to be able to handle the numerous challenges they face in their line of duty. As such, BAs can remain relevant even as businesses change quickly through continuous learning and development within these areas. The attainment of these abilities is critical for any hopeful analyst who wants to become a frontrunner in this field, whether it is via formal education, job experience, or professional courses or certifications
- Written By - Natasha Singh